GitHub Copilot Cheatsheet - Description and useful commands
Description, plans commands list and keyboard shortcuts
Here is an up-to-date GitHub Copilot cheat sheet, covering essential shortcuts, commands, usage tips, and context features for Visual Studio Code and Copilot Chat
Install GitHub Copilot in Visual Studio Code
To install GitHub Copilot in Visual Studio Code:
- Open Visual Studio Code on your system.
- Go to the Extensions View by clicking the Extensions icon on the sidebar or pressing Ctrl+Shift+X (Windows/Linux) or Cmd+Shift+X (Mac).
- Search for “GitHub Copilot” in the Extensions Marketplace search bar.
- Click “Install” on the “GitHub Copilot” extension published by GitHub.
- Sign in to GitHub: After installation, you will be prompted to sign in to your GitHub account. Authorize GitHub Copilot to access your account when prompted in a browser window.
- (If required) Enable or configure Copilot: Once signed in, you may configure Copilot to customize its behavior via the settings menu if you wish.
Prerequisites:
- VS Code must be installed on your system.
- A GitHub account with a Copilot subscription or active trial.
After setup, Copilot will be active and you should see its icon in the status bar ready to help write code. If you do not see suggestions, reload VS Code or ensure you’re signed in with an eligible account.
Keyboard Shortcuts (VS Code)
Here is a list of useful GitHub Copilot keyboard shortcuts for both Windows and Mac
| Action | macOS Shortcut | Windows/Linux Shortcut |
|---|---|---|
| Open Chat view | ⌃⌘I | Ctrl+Alt+I |
| Start inline chat (editor/terminal) | ⌘I | Ctrl+I |
| New chat session in Chat view | ⌘N | Ctrl+N |
| Switch to agent/edit mode | ⇧⌘I / Cmd+. | Ctrl+Shift+Alt+I / Ctrl+. |
| Accept inline suggestion | Tab | Tab |
| Dismiss suggestion | Escape | Escape |
| Open autocomplete suggestions | Ctrl+Enter | Ctrl+Enter |
| Accept suggestion (inline chat) | Cmd+Enter | Ctrl+Enter |
Common Slash Commands (in Chat/Inline Chat Box)
Here is a list of Standard slash commands
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| /clear | Start a new chat session / Clear conversation |
| /delete | Delete a conversation |
| /explain | Explain the current/selected code |
| /fix | Propose a fix for the selected code |
| /tests | Generate unit tests for selected code |
| /help | Get Copilot help and usage info |
| /new | Start a new project |
Chat Variables for Context
Type # followed by a variable to add specific context in prompts:
| Variable | Context Included |
|---|---|
| #block | Current code block |
| #class | Current class |
| #comment | Current comment |
| #file | Entire file content |
| #function | Current function/method |
| #line | Current line of code |
| #path | File path |
| #project | Project/workspace context |
| #selection | Current text selection |
| #sym | Current symbol |
Prompting Tips and Features
- Use @mentions to reference relevant files, issues, PRs, etc. in your chat.
- Be specific and concise in instructions for best results.
- Drag and drop files or folders into the chat pane to add context.
- Use
#context variables to focus Copilot’s answers on relevant code areas. - Choose between chat modes: ask (questions), edit (edit code), agent (autonomous workflow).
Best Practices
- Segment code into smaller functions and write good comments for better completions.
- Use chat for refactoring, generating docs, fixing test failures, or onboarding to a new codebase.
- Edit previous prompts and revert changes directly in chat, review chat history, or use voice to interact with Copilot.
Supported Languages and Environments
- Supports most popular languages: Python, JS, TypeScript, Go, Java, C#, C++, Ruby, PHP, and more.
- Available in Visual Studio Code, JetBrains IDEs, CLI, and GitHub web interface.
Additional Resources
- For frequently updated PDFs and one-page shortcuts, see community-maintained cheat sheets.
- For more examples and in-depth guides, GitHub Copilot Cookbooks and official documentation can be helpful.
For more in-depth coverage or the latest features based on your environment, visit the official documentation or GitHub repositories.
GitHub Copilot Key Features
GitHub Copilot assists in code completion across many programming languages by leveraging AI models trained on vast datasets of public code, enabling it to recognize and generate code patterns and solutions relevant to each language. As you type in your IDE (such as Visual Studio Code, Visual Studio, JetBrains IDEs, etc.), Copilot analyzes the code around your cursor, recent edits, and even natural language comments or docstrings to suggest possible completions
Key ways Copilot provides language-agnostic code completion include:
- Context Awareness: The AI understands code context, variable names, file structure, and language-specific syntax to offer relevant suggestions, whether you’re writing Python, JavaScript, C#, C++, Java, Go, TypeScript, Ruby, PHP, or other supported languages. For languages commonly found in public repositories (such as JavaScript, Python, and TypeScript), Copilot’s suggestions are especially robust.
- Inline and Block Suggestions: Copilot can provide simple single-line autocompletions or suggest whole blocks of code—such as full functions or classes—suited to the current programming language and its conventions.
- Natural Language Prompts: By interpreting comments written in plain English, Copilot can generate code in your target language that fulfills the described requirements.
- Adaptive Learning: While Copilot doesn’t update from your private code in real-time, it adapts to the immediate session’s code patterns to increase relevance within the current file and project.
- IDE Integration: Its plugins and extensions allow Copilot to be used seamlessly in popular development environments, making language switching and multi-language codebases efficient and productive.
By understanding the coding intentions and context, Copilot accelerates development workflows, supports rapid prototyping, reduces boilerplate coding, and introduces language-idiomatic solutions, streamlining tasks across diverse programming environments.
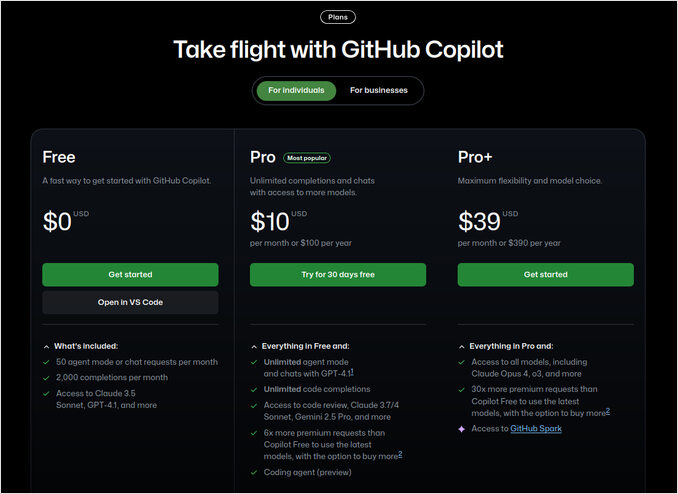
GitHub Copilot Subscription Pricing
GitHub Copilot has a tiered pricing model with options for individuals and organizations, as well as a limited free plan. Here’s a breakdown of the current pricing and plan features (as of August 2025):
Subscription Plans
| Plan | Cost | Who is it for? | Key Features/Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free | $0 | Individual exploratory use | 2,000 completions, 50 chat requests, limited models |
| Pro | $10/mo or $100/yr | Individuals, power users | Unlimited completions, 300 premium requests/mo |
| Pro+ | $39/mo or $390/yr | Power users, AI heavy users | More premium requests, all models |
| Business | $19/user/mo | Teams/organizations | All Pro features, license + policy management, admin and IP controls |
| Enterprise | $39/user/mo | Enterprises | All Business + enterprise management/features and integrations |
Premium requests: If you exceed your included premium requests, you can purchase more at $0.04/request.
Free Access
- Eligibility: Verified students, teachers, and maintainers of popular open source projects can get Copilot Pro for free after verification.
- Note: Copilot Free is not available to organization-linked accounts.
Free Trial and Billing
- 30-day free trial: New subscribers to Pro can access all features before payment. Billing requires a valid payment method and starts automatically if not canceled before trial ends.
- You can select a monthly or yearly billing cycle and change it at any time; yearly plans are discounted.
Usage & Model Limits
- All paid plans allow unlimited basic completions and chats. However, each plan includes a monthly allowance of “premium requests” for advanced models and features (e.g., code review, latest model access). Unused premium requests reset at the start of each month.
- You can monitor and manage your usage/purchasing directly in your Copilot or GitHub account settings.
References: Pricing and features may evolve, so check GitHub’s Copilot documentation for the latest updates.
Differences between Paid and Free GitHub Copilot access
The main differences between GitHub Copilot’s free and paid (Pro/Pro+) plans are the limits on usage and access to advanced features, AI models, and support. Here is a structured comparison:
| Feature | Free Plan | Paid Plans (Pro/Pro+) |
|---|---|---|
| Code Completions | 2,000/month | Unlimited |
| Chat Requests | 50/month | Unlimited (with Pro/Pro+), higher limits |
| Premium Requests | 50/month | 300/month (Pro), higher with Pro+ |
| Access to AI Models | Limited | Full access to more advanced/premium models |
| Copilot Chat | Limited | Full access |
| Intended Use | Personal/individual only | Individuals, professionals, power users |
| Upgrade Path | No subscription needed | Monthly/yearly subscription required |
| Free Access Provision | Students/teachers get Pro for free | Paid by default (except specific eligibilities) |
| Organization Use | Not available—individual only | Admin/policy controls (Business/Enterprise) |
- The free plan provides a capped experience: up to 2,000 code completions and 50 premium/chat requests per month, with only a subset of models and features. It’s strictly for personal use and not for organization-managed accounts.
- The Pro (paid) plan offers unlimited completions, more advanced AI models, Copilot Chat, up to 300 premium requests per month, and other premium features. The Pro+ raises these limits further. These benefits are essential for regular or power users who need unrestricted access to AI assistance.
- Students, teachers, and active open-source maintainers are eligible to get Pro for free with verification.
- Paid plans also provide priority for new features, premium support, and, at organizational levels (Business/Enterprise), admin and policy management tools.
In summary, the free plan is aimed at exploring Copilot with limited quotas, while paid plans remove those limits, grant access to more advanced capabilities, and support professional and organizational development workflows.
Useful links
- https://github.com/features/copilot
- https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/copilot/reference/copilot-vscode-features
- https://github.com/features/copilot/plans
- https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/github-copilot/
- GitHub Actions Cheatsheet - Standard structure and a List of most useful actions
- Gitflow Explained: Steps, Alternatives, Pros, and Cons
- DevOps with GitOps - Argo CD, Flux, Jenkins X, Weave GitOps and others
- GIT commands cheatsheet
- Gitea - installing and testing
- Backup and restore Gitea server

