Costruire un AWS Lambda a doppio modo con Python e Terraform
Esempio passo passo
Ecco un esempio di Python Lambda per il processore di messaggi SQS + API REST con protezione tramite chiave API + Terraform script per il deployment per l’esecuzione serverless.
AWS Lambda ti permette di scrivere funzioni serverless leggere che possono reagire a quasi ogni evento — dai messaggi SQS alle richieste HTTP. In questa guida, costruiremo una singola Python Lambda che funziona in due modalità:
- Modalità SQS: Quando attivata da un messaggio SQS come
{ "par": 10 }, pubblica{ "res": 11 }in un’altra coda. - Modalità HTTP: Quando chiamata tramite API Gateway a
GET /lam?par=10, restituisce{ "res": 11 }al client.
Proteggeremo anche l’estremità HTTP utilizzando una semplice chiave API hardcoded — "testkey".
L’intera configurazione verrà distribuita utilizzando Terraform.
Panoramica dell’architettura
Visualizziamo ciò che stiamo costruendo:
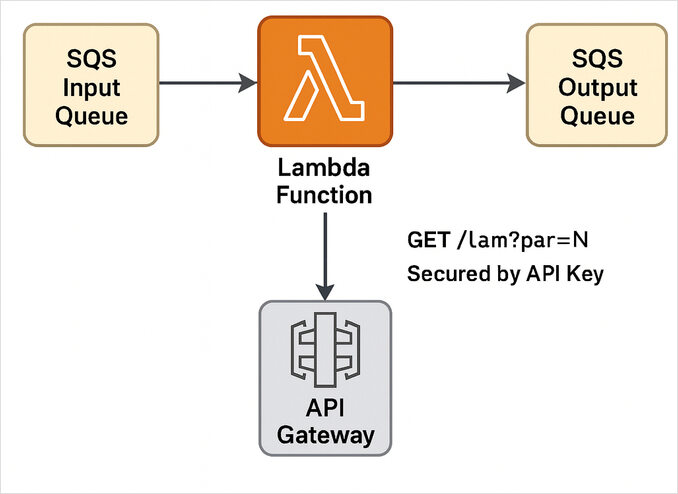
La stessa Lambda reagisce a entrambi:
- Eventi SQS, tramite una mappatura delle fonti degli eventi, e
- Richieste API Gateway, tramite un’integrazione HTTP RESTful.
Passo 1: Creare la Lambda in Python
Creiamo un gestore molto semplice in Python che possa distinguere tra un evento SQS e una chiamata HTTP.
File: lambda_function.py
import json
import os
import boto3
sqs = boto3.client("sqs")
OUTPUT_QUEUE_URL = os.environ.get("OUTPUT_QUEUE_URL")
API_KEY = os.environ.get("API_KEY", "testkey") # default hardcoded
def lambda_handler(event, context):
# Rileva il tipo di evento
if "Records" in event: # evento SQS
return handle_sqs(event["Records"])
else: # evento HTTP
return handle_http(event)
def handle_sqs(records):
for record in records:
body = json.loads(record["body"])
par = int(body["par"])
res = par + 1
message = json.dumps({"res": res})
sqs.send_message(QueueUrl=OUTPUT_QUEUE_URL, MessageBody=message)
return {"status": "processed", "count": len(records)}
def handle_http(event):
headers = {k.lower(): v for k, v in (event.get("headers") or {}).items()}
if headers.get("x-api-key") != API_KEY:
return {
"statusCode": 403,
"headers": {"Content-Type": "application/json"},
"body": json.dumps({"error": "Forbidden"})
}
params = event.get("queryStringParameters") or {}
if "par" not in params:
return {
"statusCode": 400,
"headers": {"Content-Type": "application/json"},
"body": json.dumps({"error": "Parametro mancante: par"})
}
par = int(params["par"])
return {
"statusCode": 200,
"headers": {"Content-Type": "application/json"},
"body": json.dumps({"res": par + 1})
}
Quello che abbiamo in questa funzione Lambda:
- I messaggi SQS vengono analizzati come JSON.
- Quando attivata da API Gateway, la funzione verifica la chiave API e il parametro di query.
- L’URL della coda di output e la chiave API vengono passati tramite variabili d’ambiente.
Passo 2: Deploy con Terraform
Terraform ci permette di impostare dichiarativamente l’infrastruttura AWS — Lambda, code SQS, API Gateway e permessi — in un’unica volta.
Struttura del progetto:
project/
├── lambda/
│ └── lambda_function.py
└── infra/
└── main.tf
Configurazione Terraform (infra/main.tf)
terraform {
required_providers {
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
version = "~> 5.0"
}
archive = {
source = "hashicorp/archive"
}
}
}
provider "aws" {
region = "us-east-1"
}
locals {
project = "lambda-sqs-api"
}
# Pacchetto Lambda
data "archive_file" "lambda_zip" {
type = "zip"
source_dir = "../lambda"
output_path = "lambda.zip"
}
# Code SQS
resource "aws_sqs_queue" "input" {
name = "${local.project}-input"
}
resource "aws_sqs_queue" "output" {
name = "${local.project}-output"
}
# Ruolo IAM per Lambda
data "aws_iam_policy_document" "assume_role" {
statement {
actions = ["sts:AssumeRole"]
principals {
type = "Service"
identifiers = ["lambda.amazonaws.com"]
}
}
}
resource "aws_iam_role" "lambda_role" {
name = "${local.project}-role"
assume_role_policy = data.aws_iam_policy_document.assume_role.json
}
resource "aws_iam_policy" "lambda_policy" {
name = "${local.project}-policy"
policy = jsonencode({
Version = "2012-10-17"
Statement = [
{
Effect = "Allow"
Action = [
"sqs:SendMessage",
"sqs:ReceiveMessage",
"sqs:DeleteMessage",
"sqs:GetQueueAttributes"
]
Resource = "*"
},
{
Effect = "Allow"
Action = [
"logs:CreateLogGroup",
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:PutLogEvents"
]
Resource = "*"
}
]
})
}
resource "aws_iam_role_policy_attachment" "lambda_policy_attach" {
role = aws_iam_role.lambda_role.name
policy_arn = aws_iam_policy.lambda_policy.arn
}
# Funzione Lambda
resource "aws_lambda_function" "func" {
filename = data.archive_file.lambda_zip.output_path
function_name = local.project
role = aws_iam_role.lambda_role.arn
handler = "lambda_function.lambda_handler"
runtime = "python3.12"
environment {
variables = {
OUTPUT_QUEUE_URL = aws_sqs_queue.output.id
API_KEY = "testkey"
}
}
}
# Mappatura della fonte degli eventi (SQS → Lambda)
resource "aws_lambda_event_source_mapping" "sqs_trigger" {
event_source_arn = aws_sqs_queue.input.arn
function_name = aws_lambda_function.func.arn
batch_size = 1
enabled = true
}
# API Gateway
resource "aws_api_gateway_rest_api" "api" {
name = "${local.project}-api"
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_resource" "lam" {
rest_api_id = aws_api_gateway_rest_api.api.id
parent_id = aws_api_gateway_rest_api.api.root_resource_id
path_part = "lam"
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_method" "get_lam" {
rest_api_id = aws_api_gateway_rest_api.api.id
resource_id = aws_api_gateway_resource.lam.id
http_method = "GET"
authorization = "NONE"
api_key_required = true
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_integration" "lambda_integration" {
rest_api_id = aws_api_gateway_rest_api.api.id
resource_id = aws_api_gateway_resource.lam.id
http_method = aws_api_gateway_method.get_lam.http_method
integration_http_method = "POST"
type = "AWS_PROXY"
uri = aws_lambda_function.func.invoke_arn
}
resource "aws_lambda_permission" "api_gateway" {
statement_id = "AllowAPIGatewayInvoke"
action = "lambda:InvokeFunction"
function_name = aws_lambda_function.func.function_name
principal = "apigateway.amazonaws.com"
source_arn = "${aws_api_gateway_rest_api.api.execution_arn}/*/*"
}
# Chiave API e piano d'uso
resource "aws_api_gateway_api_key" "key" {
name = "testkey"
value = "testkey"
enabled = true
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_usage_plan" "plan" {
name = "basic"
api_stages {
api_id = aws_api_gateway_rest_api.api.id
stage = aws_api_gateway_deployment.deploy.stage_name
}
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_usage_plan_key" "plan_key" {
key_id = aws_api_gateway_api_key.key.id
key_type = "API_KEY"
usage_plan_id = aws_api_gateway_usage_plan.plan.id
}
resource "aws_api_gateway_deployment" "deploy" {
depends_on = [aws_api_gateway_integration.lambda_integration]
rest_api_id = aws_api_gateway_rest_api.api.id
stage_name = "v1"
}
output "api_url" {
value = "${aws_api_gateway_deployment.deploy.invoke_url}/lam"
}
Passo 3: Deploy e Test
- Inizializza Terraform:
cd infra
terraform init
- Applica la configurazione:
terraform apply
- Testa l’estremità API Gateway:
curl -H "x-api-key: testkey" "<API_URL>?par=10"
# Risultato atteso: {"res": 11}
- Testa SQS:
Invia un messaggio alla coda di input:
aws sqs send-message --queue-url <input-queue-url> --message-body '{"par": 5}'
Poi controlla la coda di output:
aws sqs receive-message --queue-url <output-queue-url>
# Risultato atteso: {"res": 6}
Passo 4: Pulizia
Per rimuovere tutti i risorse:
terraform destroy
Riepilogo
[Coda di Input SQS] ─▶ [Funzione Lambda] ─▶ [Coda di Output SQS]
▲
│
[API Gateway /lam?par=N]
│
Protetta da chiave API
Hai appena costruito una Lambda multi-trigger che:
- Consuma da e pubblica su code SQS.
- Risponde a richieste HTTP tramite API Gateway.
- Applica una chiave API tramite un semplice controllo dell’intestazione.
- È completamente gestita tramite Terraform per un’infrastruttura serverless riproducibile.

Questo modello è molto utile per trasformatori di messaggi leggeri, microservizi ibridi o per collegare sistemi AWS asincroni e sincroni — tutto con poche righe di Python e Terraform.
Se vorresti vedere un esempio un po’ più avanzato di Lambda utilizzando AWS SAM — per favore controlla questo post: Coding Lambda utilizzando AWS SAM + AWS SQS + Python PowerTools
Link utili
- Python Cheatsheet
- Terraform cheatsheet - comandi utili ed esempi
- Prestazioni di AWS Lambda: JavaScript vs Python vs Golang
- Lambda stratificate con AWS SAM e Python
- Coding Lambda utilizzando AWS SAM + AWS SQS + Python PowerTools
- Panoramica su AWS CDK, esempi in TypeScript e Python e considerazioni sulle prestazioni

