
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Tutorial: Architecture, Implementation, and Production Guide
From basic RAG to production: chunking, vector search, reranking, and evaluation in one guide.

From basic RAG to production: chunking, vector search, reranking, and evaluation in one guide.



Control data and models with self-hosted LLMs
Self-hosting LLMs keeps data, models, and inference under your control-a practical path to AI sovereignty for teams, enterprises, nations.

LLM speed test on RTX 4080 with 16GB VRAM
Running large language models locally gives you privacy, offline capability, and zero API costs. This benchmark reveals exactly what one can expect from 9 popular LLMs on Ollama on an RTX 4080.

January 2026 trending Python repos
The Python ecosystem this month is dominated by Claude Skills and AI agent tooling. This overview analyzes the top trending Python repositories on GitHub.

January 2026 trending Rust repos
The Rust ecosystem is exploding with innovative projects, particularly in AI coding tools and terminal applications. This overview analyzes the top trending Rust repositories on GitHub this month.

January 2026 trending Go repos
The Go ecosystem continues to thrive with innovative projects spanning AI tooling, self-hosted applications, and developer infrastructure. This overview analyzes the top trending Go repositories on GitHub this month.

Choose the right Python package manager
This comprehensive guide provides background and a detailed comparison of Anaconda, Miniconda, and Mamba - three powerful tools that have become essential for Python developers and data scientists working with complex dependencies and scientific computing environments.
Self-hosted ChatGPT alternative for local LLMs
Open WebUI is a powerful, extensible, and feature-rich self-hosted web interface for interacting with large language models.

Melbourne's essential 2026 tech calendar
Melbourne’s tech community continues to thrive in 2026 with an impressive lineup of conferences, meetups, and workshops spanning software development, cloud computing, AI, cybersecurity, and emerging technologies.

Fast LLM inference with OpenAI API
vLLM is a high-throughput, memory-efficient inference and serving engine for Large Language Models (LLMs) developed by UC Berkeley’s Sky Computing Lab.
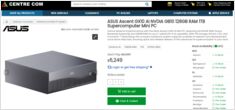
Real AUD pricing from Aussie retailers now
The NVIDIA DGX Spark (GB10 Grace Blackwell) is now available in Australia at major PC retailers with local stock. If you’ve been following the global DGX Spark pricing and availability, you’ll be interested to know that Australian pricing ranges from $6,249 to $7,999 AUD depending on storage configuration and retailer.

Technical guide to AI-generated content detection
The proliferation of AI-generated content has created a new challenge: distinguishing genuine human writing from “AI slop” - low-quality, mass-produced synthetic text.

Testing Cognee with local LLMs - real results
Cognee is a Python framework for building knowledge graphs from documents using LLMs. But does it work with self-hosted models?

Type-safe LLM outputs with BAML and Instructor
When working with Large Language Models in production, getting structured, type-safe outputs is critical. Two popular frameworks - BAML and Instructor - take different approaches to solving this problem.